Oracle Database Licensing
What is an Oracle Database License?
An Oracle database licensing / license is a legal agreement that allows an organization to use Oracle database software. Oracle is a leading provider of database software, which is used to store, organize, and manage large amounts of data.
The terms of an Oracle database license typically specify how the software can be used, how many users can access the database, and the length of time the license is valid. Oracle offers a variety of licensing options, including perpetual licenses and subscription-based licenses.
Perpetual licenses allow an organization to use the Oracle database software indefinitely, as long as the terms of the license are met. Subscription-based licenses, on the other hand, allow an organization to use the software for a specified period of time, after which the license must be renewed in order to continue using the software.
In addition to these types of licenses, Oracle also offers a number of different licensing models, including processor-based licensing, named user plus licensing, and metric-based licensing. The specific licensing model that an organization chooses will depend on a number of factors, including the size of the organization, the type of database environment it has, and the specific needs of the organization.
It’s important for organizations to carefully review the terms of an Oracle database license before using the software, as failure to comply with the terms of the license could result in legal penalties.
Oracle Database Licensing Instructions
Typical Database Software Environments
- Production Environment
- Test Environment
- Development Environment

Why are there different environments? Today’s software environments are complex, particularly with the integration of the web, the proliferation of corporate extranets, and the increased usage of corporate self-service applications. To ensure data integrity and security, companies often utilize multiple database instances to manage their application development environments.
Database Environments As a general rule, Oracle’s pricing practices do not restrict the number of database instances a customer installs on a server, nor do they differentiate between single server and networked environments. Multiple environments may be installed on the same server. All users of all environments must be properly licensed.
Development Environment: Customers may use Oracle Full Use licenses in a development environment. Customers also may download Oracle Database products from the Oracle Technology Network (OTN) at http://otn.oracle.com. In order to download the Oracle Database product from OTN, customers must accept the terms of the OTN License Agreement. Subject to the full terms of the OTN License Agreement, this limited license allows the user to develop applications using the licensed products as long as such applications have not been used for any data processing, business, commercial, or production purposes. Customers may not use Oracle Database, as licensed under the OTN License Agreement, in connection with any classroom activity, internal data processing operations, or any other commercial or production use purposes. The OTN License Agreement is a limited license, and is not part of any other Oracle agreement such as the Oracle Master Agreement (OMA) or Oracle License and Services Agreement (OLSA). If a customer wants to use Oracle Database, as licensed under the OTN License Agreement, for any purposes other than the limited development rights granted by that license, including deployment of an application developed under an OTN License Agreement, he will need to contact Oracle, or an authorized Oracle reseller, to obtain the appropriate licenses.
Test Environment: All programs used in a test environment must be licensed under an OMA, OLSA, or other appropriate Oracle (or Oracle authorized reseller) license agreement.
Production Environment: The environment used by end users for business or other operations is called a production environment. All programs used in the production environment must be licensed under an OMA, OLSA, or other appropriate Oracle (or Oracle authorized reseller) license agreement.
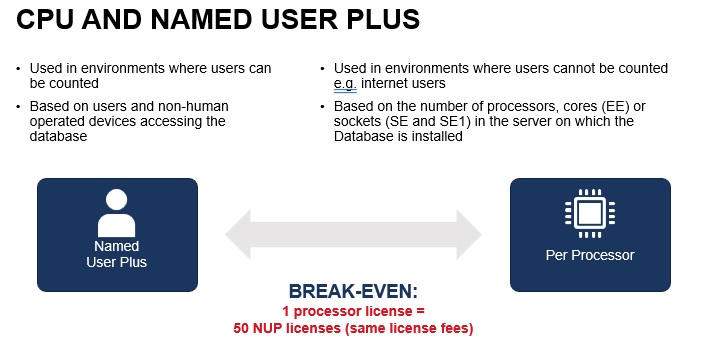
Database Metrics – The Oracle Standard Edition 2 and Enterprise Edition of the database can be licensed using the Named User Plus metric or the Processor metric. The Personal Edition can only be licensed using the Named User Plus metric. In this section, we review the benefits associated with each metric.
Named User Plus: This metric can be used in all environments. Different minimums apply depending on the Database edition:
- Oracle Database Standard Edition 2 may only be licensed on servers that have a maximum capacity of 2 sockets. In addition, notwithstanding any provision in Your Oracle license agreement to the contrary, each Oracle Database Standard Edition 2 database may use a maximum of 16 CPU threads at any time. The minimums when licensing by Named User Plus (NUP) metric are 10 NUP licenses per server.
- The Enterprise Edition requires a minimum of 25 Named User Plus per Processor licenses or the total number of actual users, whichever is greater.

Example: A customer who wants to license the Database Enterprise Edition on a 4-way box (assuming single core chips) will be required to license a minimum of 4 processors * 25 Named User Plus, which is equal to 100 Named User Plus. When licensing the Oracle Database by Named User Plus, all users who are using the Oracle Database, as well as all non-human operated devices that are accessing the Oracle Database must be licensed. The following licensing rules apply:
- If non-human operated devices such as sensors are connecting to the Oracle Database, then all devices need to be licensed.
- If human-operated devices such as bar code scanners are connecting to the Oracle Database, then all humans operating these devices need to be licensed.
- If non-human operated devices and human-operated devices are connecting to the Oracle Database and are mutually exclusive, then all non-human devices and all humans operating devices need to be licensed.
Processor: This metric is used in environments where users cannot be identified and counted. The Internet is a typical environment where it is often difficult to count users. This metric can also be used when the Named User Plus population is very high and it is more cost effective for the customer to license the Database using the Processor metric. The Processor metric is not offered for Personal Edition. The number of required licenses shall be determined by multiplying the total number of cores of the processor by a core processor licensing factor specified on the Oracle Processor Core Factor Table which can be accessed at http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/contracts/processor-corefactor-table-070634.pdf. All cores on all multicore chips for each licensed program are to be aggregated before multiplying by the appropriate core processor licensing factor and all fractions of a number are to be rounded up to the next whole number. When licensing Oracle programs with Standard Edition One, Standard Edition 2 or Standard Edition in the product name, a processor is counted equivalent to a socket; however, in the case of multi-chip modules, each chip in the multi-chip module is counted as one occupied socket.

For example, a multicore chip based server with an Oracle Processor Core Factor of 0.25 installed and/or running the program (other than Standard Edition One programs or Standard Edition programs) on 6 cores would require 2 processor licenses (6 multiplied by a core processor licensing factor of .25 equals 1.50, which is then rounded up to the next whole number, which is 2). As another example, a multicore server for a hardware platform not specified in the Oracle Processor Core Factor Table installed and/or running the program on 10 cores would require 10 processor licenses (10 multiplied by a core processor licensing factor of 1.0 for ‘All other multicore chips’ equals 10).
Note on Minimums: Product Minimums for Named User Plus licenses (where the minimums are per processor) are calculated after the number of processors to be licensed is determined, using the processor definition
How much does an Oracle Database license cost?
The cost of an Oracle database license can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the type of license, the number of users, and the type of database environment. Oracle Database Enterprise Edition Processor license costs $ 47,500 and Oracle Database Standard Edition 2 costs $ 17,500 per processor.
In general, Oracle database licenses tend to be more expensive than licenses for other database software. This is due in part to the fact that Oracle is a leading provider of database software and has a strong reputation for reliability and performance.
The specific cost of an Oracle database license will depend on the specific needs of the organization, as well as the terms of the license. Oracle offers a number of different licensing options, including perpetual licenses and subscription-based licenses, and a variety of different licensing models, including processor-based licensing, named user plus licensing, and metric-based licensing.
Oracle Licensing FAQ
How does Oracle licensing work?
Oracle technology products are licensed per processor which means you count the occupied processor cores and or the number of cores in the specific server. Named User Plus is also available to license Oracle technology products.
Oracle application products are generally licensed per user or per company revenue.
How is Oracle license calculated?
Start by reviewing which product you need then review if you need a processor or named user plus license. Then apply Oracle core factor table to calculate the number of licenses. If you are unsure about your licensing, get expert help.
How to check licenses in Oracle?
You can request a license inventory list from Oracle, or review the latest Oracle support renewal.
How to activate Oracle license?
For Oracle products, do not need a license key or activate the product.
Licensing Oracle in disaster recovery environments
In today’s data and information intensive economy, businesses need continuous access to mission-critical information. IT departments must not only manage the rapid growth of business information but they must also keep this information available and protected. That’s why every business has data recovery and business continuance plans. This document will help you in understanding how to license Oracle programs in such environments. Data Recovery environments are usually deployed using the following two methods: a) Deploying a clustered environment such as Failover or b) Copying, Synchronizing or Mirroring of the data and/or program files (such as Physical DB files, Binaries, Executables).
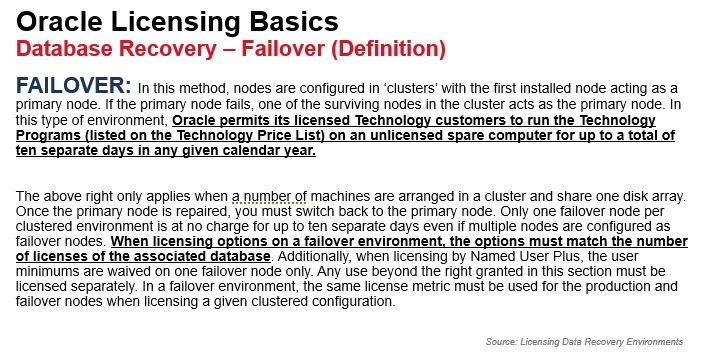
Data Recovery using Clustered Environments (Failover) The failover data recovery method is an example of a clustered deployment, where multiple nodes/servers have access to one Single Storage/SAN. In such cases your license for the programs listed on the US Oracle Technology Price List (http://www.oracle.com/corporate/pricing/pricelists.html) is eligible for the 10-day rule, which includes the right to run the licensed program(s) on an unlicensed spare computer in a failover environment for up to a total of ten separate 24-hour periods in any given calendar year (for example, if a failover node is down for two hours on Tuesday and three hours on Friday, it counts as two 24-hour periods).
The above right only applies when a number of physical or logical machines as defined in Oracle’s Partitioning Policy (detailed in https://www.oracle.com/assets/partitioning-070609.pdf) are arranged in a cluster and share one logical disk array located in a single data center. When the primary node fails, the failover node acts as the primary node. Once the primary node is repaired, you must either switch back or designate that repaired server as the failover node. Once the failover period has exceeded ten 24-hour periods, the failover node must be licensed. In addition, only one failover node per clustered environment is at no charge even if multiple nodes are configured as failover.
Downtime for maintenance purposes counts towards the ten separate 24-hour periods limitation. When licensing options on a failover environment, the options must match the number of licenses of the associated database. Additionally, when licensing by Named User Plus, the user minimums are waived on one failover node only. Any use beyond the right granted in this section must be licensed separately. In a failover environment, the same license metric must be used for the production and failover nodes when licensing a given clustered configuration.
Data Recovery Environments using Copying, Synchronizing or Mirroring Standby and Remote Mirroring are commonly used terms to describe these methods of deploying Data Recovery environments. In these Data Recovery deployments, the data, and optionally the Oracle binaries, are copied to another storage device. In these Data Recovery deployments all Oracle programs that are installed and/or running must be licensed per standard policies documented in the Oracle Agreement. This includes installing Oracle programs on the DR server(s) to test the DR scenario. Licensing metrics and program options on Production and Data Recovery servers must match with two exceptions: 1) Real Application Clusters (RAC) – Oracle RAC does not need to be licensed on the Data Recovery server unless used on the Data Recovery server; 2) For Production servers licensed using one of the Oracle Data Management Cloud Services listed in this document (http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/contracts/paas-iaas-universal-credits-3940775.pdf), only program options in use on the Production server must be licensed on the Data Recovery server.
Testing For the purpose of testing physical copies of backups, your license for the Oracle Database includes the right to run the database on an unlicensed computer for up to four times, not exceeding 2 days per testing, in any given calendar year. The aforementioned right does not cover any other data recovery method – such as remote mirroring – where the Oracle program binary files are copied or synchronized.
If you need help with Oracle database licensing we have experts available to help you. Contact us to find out more.