
- Oracle on AWS – Why Oracle doesn't like it
- What is AWS EC2, and how to license Oracle?
- What is AWS RDS for Oracle?
- To summarize AWS RDS Oracle.
- AWS Baremetal Solutions
- How to calculate Oracle Licensing on AWS
- Oracle on AWS Licensing Benefits
- Oracle on AWS License Compliance issues
- Oracle Licensing in AWS – Top5 compliance issues seen.
- FAQ Oracle licensing on AWS:
- Oracle license AWS Oracle licensing
Oracle on AWS – Why Oracle doesn’t like it
Oracle on AWS? Oracle doesn’t want you to move to AWS; then wants you to move to their cloud, which makes it very important for you to be compliant when you move to AWS. When moving your Oracle licenses to AWS, you have two options, either deploy on EC2 and count the licenses correctly and understand the licensing policies. The second option is RDS which AWS has a license that includes some options. Most of our clients choose EC2 and bring their own licenses.
To understand Oracle licensing on Amazon Web Services (AWS), it is necessary to understand how Oracle licensing works in the cloud in general. Oracle has designated two public cloud platforms, Microsoft Azure and AWS, as authorized public cloud providers and has provided special licensing rules for Oracle customers using these platforms. If you are using any other public cloud provider, the normal on-premises Oracle licensing rules apply. It is important to note that Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is not an authorized cloud provider, and there is no difference in the way Oracle is licensed on GCP compared to any traditional hosting provider. This article aims to assist you with licensing Oracle on AWS, including both AWS EC2 and AWS RDS for Oracle.
What is AWS EC2, and how to license Oracle?
- AWS EC2 (Amazon Web Services Elastic Compute Cloud) is a cloud computing service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud.
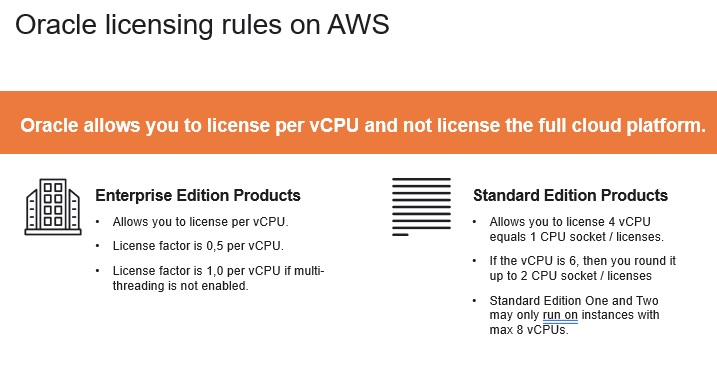
- Oracle’s Core Factor Table outlines the number of Oracle licenses required for different CPU architectures. This table is not subject to Oracle’s Cloud Licensing Policy, so each core counts towards the number of required Oracle licenses. This policy applies to EC2 instances running Oracle applications and databases that are licensed based on the number of vCPUs.
- You can transfer an existing Oracle license to AWS instances to avoid the cost of purchasing new licenses. However, Oracle may change its licensing policy without notice, so it is important to check regularly for updates.
- With Oracle Standard Edition, you should only 4 vCPUs CPU . However, Oracle Enterprise Edition you count number of vCPUs multiplied by 0,5
What is AWS RDS for Oracle?
- AWS RDS for Oracle is a service that allows you to run your database on Amazon EC2, providing full control over your infrastructure, database environment, and operating system.
- You can choose which tools you use to manage your database and select optional modules, but you need to have a good understanding of all components and how to optimize performance.
- AWS RDS provides you with an Oracle license, which means you do not need to bring your own license or purchase one from Oracle.
- AWS is an approved cloud vendor for Oracle, so your existing Oracle licenses will work on Amazon RDS instances.
- The AWS RDS for Oracle licensing documentation contains the latest rules and regulations for licensing.
- AWS RDS offers various options for tuning and diagnosing your Oracle database, including different physical CPU models and instance types with preconfigured configurations of vCPUs, memory, storage, and networking capacity.
- The Memory Optimized instance type, particularly the R5B model, is especially beneficial for performance monitoring due to its high I/O throughput.
- You must follow Oracle technical support policies when using AWS for RDS.
Amazon RDS for Oracle supports the following Oracle license models:
- BYOL (Bring Your Own License): With this option, you can use your own Oracle licenses to run Oracle on Amazon RDS. This option is suitable for customers who already have Oracle licenses and want to use them on Amazon RDS.
- License Included: With this option, you do not need to bring your own Oracle licenses. The cost of the Oracle license is included in the hourly rate for the Amazon RDS instance. This option is suitable for customers who do not have Oracle licenses or want to use Amazon RDS without the hassle of managing Oracle licenses.
To summarize AWS RDS Oracle.
AWS RDS Oracle works like this:
- Amazon RDS for Oracle is a fully managed Oracle database service provided by AWS. AWS takes care of database management tasks such as hardware provisioning, software patching, setup, and backups.
- You must follow Oracle licensing policies for software products in public cloud environments, as outlined in the document “Licensing Oracle software in the cloud computing environment.”
- AWS RDS for Oracle is available in two options: license included or brought your own license.
- For the license included option, Oracle Database Standard Edition One and Two are available.
- For the bring your own license option, Oracle Database EE, SE2, and SE1 are available.
- If you have AWS DR (Disaster Recovery) sites, you will need to fully license all Oracle instances at both sites.
- For Java licensing on AWS, you only need to license per vCPU.
AWS Baremetal Solutions
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides customers with the option of running Oracle on Amazon EC2 Bare Metal, allowing them to benefit from AWS’s support and scalability while also accessing high-end performance. This option is generally well-suited for customers operating on a large scale and offers licensing advantages over AWS. It is important to note that Oracle on AWS is considered a hosting partner rather than a cloud provider.
For Oracle licensing, it means that you need to treat licensing like you would do on-premise.
How to calculate Oracle Licensing on AWS
- Determine the number of vCPUs that the Oracle software will be run on
- If multi-threading is enabled:
- Two vCPUs will count as one processor license
- If multi-threading is not enabled:
- Each vCPU will count as one processor license
- This calculation applies to all core-based Oracle software products.
For example:
- If you plan to run Oracle Database Enterprise Edition on an eight vCPU instance with multi-threading enabled, you will need to purchase four processor licenses.
- If you plan to run the same software on the same eight vCPU instances with multi-threading disabled, you will need to purchase eight processor licenses.
Oracle on AWS Licensing Benefits
Here are the benefits of licensing Oracle on AWS:
- You can license the capacity you need to be based on vCPU.
- Oracle’s licensing policy for virtualization (licensing all physical hosts) does not apply.
Oracle on AWS License Compliance issues
- Check your territory clause in the Oracle Ordering Document to see if you are allowed to deploy Oracle in the AWS region you are considering.
- Review your licensing agreement for any other restrictions that may prevent you from deploying in AWS.
- Oracle Database Standard Edition 2 can only be licensed on an AWS instance with a maximum of 8 vCPUs.
- Oracle ULA (Unlimited License Agreement) may not allow you to include AWS deployments in your exit numbers. Check the certification clause in your Oracle ULA for details.
Oracle Licensing in AWS – Top5 compliance issues seen.
We help many organizations with Oracle migrations to AWS, and these are the top5 compliance issues we see.
- Deploying Oracle Database Standard Edition One or Two on an AWS instance with more than eight vCPUs. Oracle’s cloud licensing policy limits the size of the AWS instance that can run these versions to a maximum of 8 vCPUs. If you install them on an instance with more vCPUs, you will need to license the Enterprise Edition.
- Counting named user plus licenses incorrectly when using Oracle Database SE2 on AWS. Oracle requires a minimum of 10 user licenses per 8 vCPUs for SE2 deployments, even if you only have five users. This requirement applies to both on-premises and cloud deployments.
- Using Oracle Enterprise Management options on Standard Edition databases on AWS. The Diagnostic and Tuning pack options are Enterprise Edition options and are not available for Standard Edition databases. However, there are no technical limitations to using these products to manage your Standard Edition database. If Oracle audits your company and discovers any current or historical usage of these options, you will be required to license the Enterprise Edition. You can use Oracle license compliance scripts to identify any unlicensed usage of database options.
- Using AWS RDS (license included) to host a proprietary application. The Oracle license included with AWS RDS is only for internal business operations and is only valid for one entity (you). You are not allowed to extend usage or access to third-party legal entities. For example, using the license-included option as a SaaS solution is not allowed. The license included option only includes standard terms.
- Bringing your own license (BYOL) to AWS RDS without reviewing your Oracle licensing agreements. When you bring your own license to AWS RDS, the same licensing terms that apply on-premises also apply to your deployment in AWS. There may be limitations on how you can use and deploy Oracle software. Be sure to review your Oracle Ordering Document to understand if there are any terms that prevent you from using your licenses in AWS RDS.
FAQ Oracle licensing on AWS:
Q: Can I deploy Oracle ULA software on AWS?
A: Yes, but there may be restrictions on the number of licenses you can bring with you when the Oracle ULA expires. The Oracle ULA certification process outlines the specific terms of your contract, as most contracts are customized.
Q: Can I bring my Oracle EBS licenses and deploy them on AWS?
A: Yes, but you should review your contract for any restrictions. In general, it is fine to deploy EBS on AWS, but be sure to comply with your user privileges, as Oracle may audit you if you deploy on AWS instead of OCI or Fusion.
Q: Oracle WebLogic on AWS how does licensing work? Weblogic licensing?
A: You use the same licensing method as for database, you count vCPUs in the same way for Weblogic Standard as you do for enterprise products on a vCPU basis.
Q: How to count Java Licensing on AWS?
A: You can count the number of Java vCPUs as enterprise licensing, counting vCPUs.
Q: What is AWS CPU optimization?
A: AWS CPU optimization is a way for AWS customers to shape EC2 instance shapes based on their requirements. As most Oracle SQL workloads are not CPU-core intensive, building your own instances can help lower Oracle licensing costs. However, Oracle does not agree with limiting the vCPUs per instance.
Oracle license AWS Oracle licensing
If you are not planning to move to the Oracle cloud, you should be particularly careful about how you license Oracle on AWS. Oracle is looking for ways to persuade you to move to their cloud, and one way they may do this is by making Oracle licensing on AWS more expensive. You should view AWS as any other hosting provider, with the exception of how you license Oracle on the hardware. Carefully review your Oracle licensing terms to understand if there are any restrictions on moving Oracle workloads to AWS. Make sure you are following all of Oracle’s licensing rules and policies by reviewing them. It is usually easy to resolve any issues before an Oracle audit.
How can we help
We offer to help organizations review Oracle licensing and ensure compliance when moving to AWS:
- Reviewing and interpreting Oracle licensing agreements to understand the terms and conditions of using Oracle software on AWS
- Identifying any potential compliance issues or areas of risk
- Providing recommendations for optimizing Oracle licensing to save money on AWS
- Assisting with the process of migrating Oracle workloads to AWS, including ensuring that all necessary licenses are in place
- Providing ongoing support and guidance to ensure that the organization remains compliant with Oracle licensing rules and policies on AWS
.
1 thought on “Oracle on AWS – The Top 5 Oracle Compliance Mistakes”
Comments are closed.